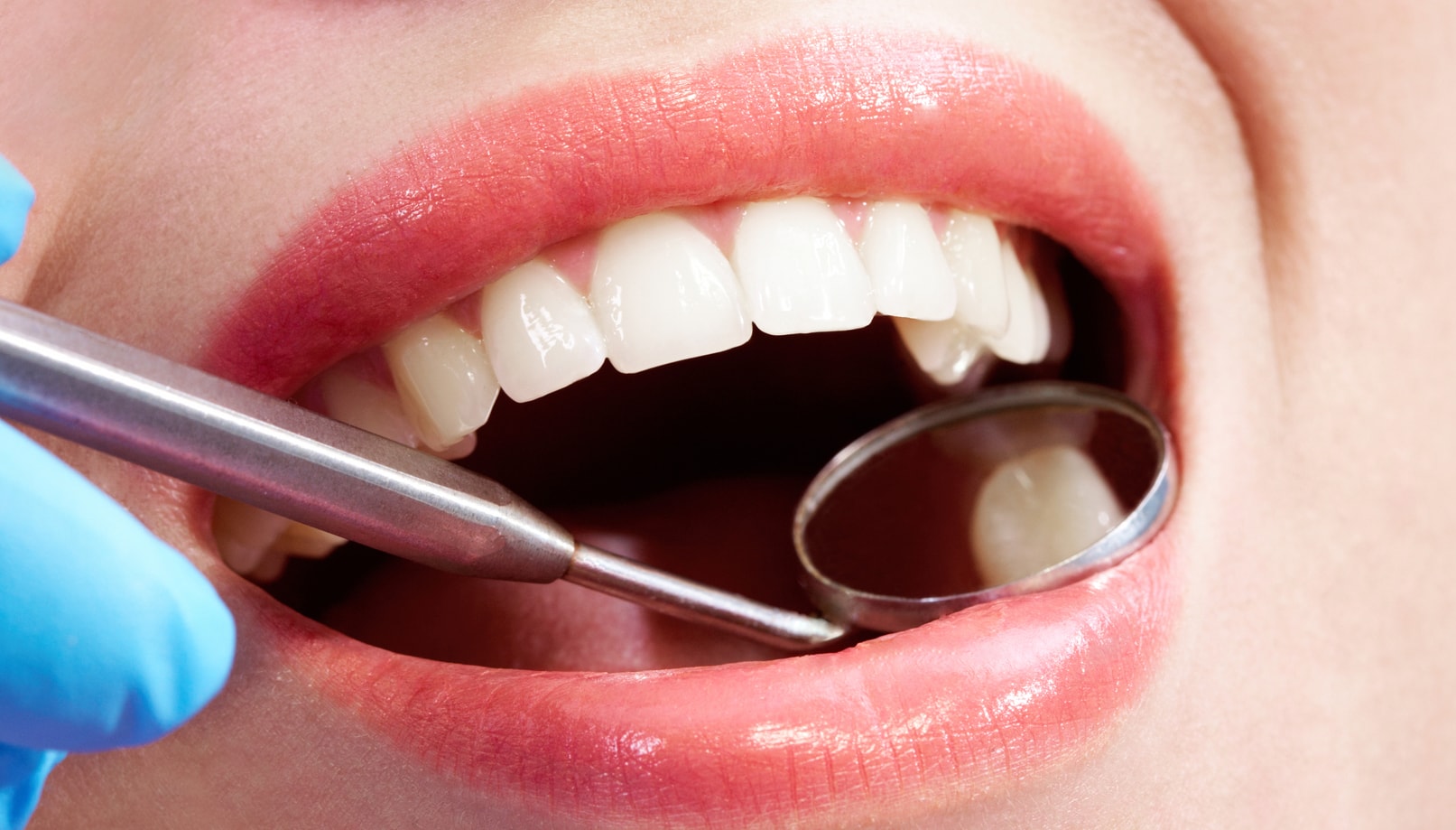
Dental fillings restore teeth damaged by decay. The filling material is made of tooth colored composite resin material to match the natural tooth color. A curing light bonds the filling to the tooth’s structure and the dentist reshapes the tooth. With direct fillings, the chosen material is immediately used to fill the cavity. With indirect fillings, the dentist takes an impression of the mouth and restorations are created. Indirect fillings are done as either inlays (performed when the tooth needs repaired within the cusps or bumps of the tooth) or onlays (covers the entire chewing surface to protect the cusps on the surface).